Indian Rice, Soybeans & Spices: A Complete Exporter’s Handbook
India has historically positioned itself at the junction of its cultural traditions and trade, with a large agricultural sector being fundamental to its economy. Indian Food Products, particularly rice, soybeans, and spices, have become the most in-demand commodities to export in India today. Filling a function of blending culture and modern-day industries, they help to situate India’s role in the global food supply chain.
This handbook contains a discussion of the opportunities and challenges for exporters, in terms of both the magnitude of opportunity and practical aspects of sourcing, compliance, and global positioning.
India’s Agricultural Legacy in Global Trade
Agriculture is a major contributor to India’s economy, and food exports are always among the top contributors to revenue. From spice routes that date back a century ago to free trading agreements today, the nation’s food products have always stocked global kitchens.
Three reasons why Indian Food Products have become the Choice of the World
- A diversity of crops, from high-end basmati rice to protein-rich soybeans, and an array of spices.
- Cost-competitive – lower production costs than developed nations.
- Quality standards – Government initiatives are underway to set standardized grades and ensure continuous compliance with quality standards.
Indian Rice: The Global Staple
Rice is India’s top export, with strong demand for both basmati and non-basmati varieties. Indian rice is now established in many markets such as the Middle East, Europe, and Africa.
- Basmati rice has become popular for its size, aroma, and cooking quality.
- Non-basmati varieties are popular in the bulk trading market for mass consumption.
Exporters who rely on rice face challenges around water-intensive forms of cultivation for quality, price fluctuations, and shifting trade barriers. But the trend toward healthy rice around the world, organic, brown, and fortified, creates growth opportunities.
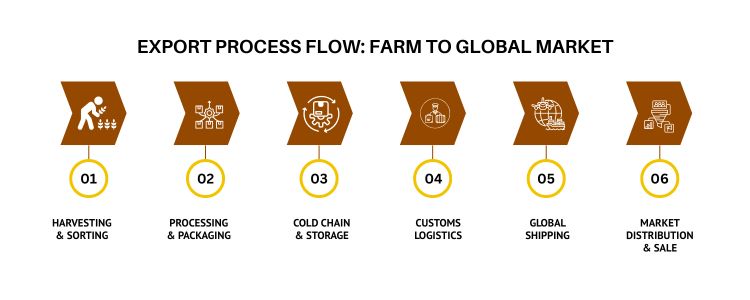
Indian Soybeans: The Protein Frontier
There is a fundamental growth in the demand for protein globally, and Indian soybeans are increasingly part of that conversation. Soy products in the form of oil, meal, and textured proteins are being consumed increasingly in Asia and Europe.
While the U.S.A. and, to some degree, Brazil continue to dominate large-scale production, India’s competitive advantage is its price and availability to growing markets. Exporters also need to be aware of price volatility on the world market and on domestic consumption that may prompt export restrictions.
Indian Spices: The Timeless Commodity
India’s standing as the world’s spice capital is undisputed, as spices such as pepper, turmeric, cardamom, cumin, and chili have sustained a great international demand in the marketplace. Indian spices are not just ingredients; they hold cultural importance and have therapeutic benefits. Among consumers demanding natural remedies and cleaner-label products, spices maintained a level of popularity in the developed markets. It was noted that there was a need for their quality assurance. Exporters need to have modern processing units to ensure pesticide residue levels are low and are compliant with food safety standards in the European Union and the United States.
The Role of Indian Sourcing Companies
Many global buyers face challenges in navigating India’s convoluted supply chain. This is where an Indian Sourcing Company is valuable. Acting as an intermediary, these companies facilitate contact between farmers, processors, and international buyers.
Indian Sourcing Companies have the expertise in:
- Sourcing reliable suppliers
- Undertaking quality checks
- Managing documentation and compliance
- Arranging logistics while mitigating risk and building trust
- Enabling ease of access to Indian products.
Global Product Sourcing: Opportunities & Trends
The landscape of Global Product Sourcing has changed in recent years. Multinational food companies and retailers are targeting India for lower-cost, higher-volume sourcing.
Some of the trends we can see include:
- Digital Integration – Blockchain and traceability systems are now commonplace.
- Sustainability – Buyers are now considering the sourcing of ingredients based on environmentally sustainable farming practices and fair-trade sourcing.
- Diversification – More younger buyers are starting to source additional new regions (Eastern Europe, Africa, etc.).
Export Regulations and Compliance
The export environment is complicated by the necessity to understand legal frameworks. In India, the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) is the principal governing agency.
For exporters, there are some considerations, including:
- Obtaining licenses and certifications for exporting (ISO, HACCP, Halal, Organic)
- Adhering to country-specific pesticide and residue requirements
- Documentation for customs and shipping
- Understanding tariff and non-tariff barriers
Failing to comply with these expectations could lead to consequences, penalties, or loss of reputation in the long run.
Exporting agricultural commodities presents its challenges. Important challenges include the following:
- Infrastructure gaps – There are inconsistencies with cold storage and logistics.
- Price fluctuations – Price variations are attributed to changing climates and global demand.
- Trade policy uncertainty – Export bans or caps disrupt planning.
The only way to solve these challenges is with investments in technology, storage, and forward contracts.
Strategic Markets for Exporters
Strategic Markets for Exporters
- Middle East: High demand for rice and spices.
- Europe: Growing demand for organic and specialty food items.
- Africa: Price-sensitive markets that can take advantage of bulk buying.
- North America: A Growing population of health-conscious consumers.
Diversification within the markets mentioned will help exporters lessen risk.
Practical Tips for Export Success
- Explore Technology: From precision agriculture to machine learning-based logistics, digital tools are helping bring efficiencies.
- Develop Strong Networks: Partner with trade groups, chambers of commerce, and international fairs.
- Long-term Branding: Value-added packaging and storytelling create shelf presence overseas.
- Ensure Consistency: Repeat business is fueled by consistent quality and timely delivery.
Conclusion
The global demand for Indian Food Products is continuously growing. Most notably, rice is a staple diet for millions of consumers, soybeans are driving demand for protein, and spices are enhancing the culinary experience worldwide. India’s agricultural exports are an essential component of the global marketplace.
However, exporters need to balance opportunity with responsibility. In the future, the question of quality, compliance, and adaptability will determine who becomes a preferred partner in this competitive landscape.
For the companies that would like to overcome challenges and invest in durability, the future of Indian exports promises not only profits but a long-lasting agreement with partners around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
They are structured services to support businesses in finding, evaluating, and managing suppliers to optimize costs, quality, and compliance.
It provides access to competitive manufacturing capabilities while being able to adapt to changing consumer needs.
Pharmaceuticals sourcing is compliance-driven, and an acknowledgment is needed for rules and standards to be met that are often above safety regulations.
Agents act as intermediaries to find and connect businesses with reputable suppliers, negotiate pricing, lead times, and mailing logistics.
Agencies provide solutions from supplier vetting to managing compliance and scaling.
No, even small and medium-sized enterprises (SME’s) see great benefit, especially when growing internationally or within regulated industries.









